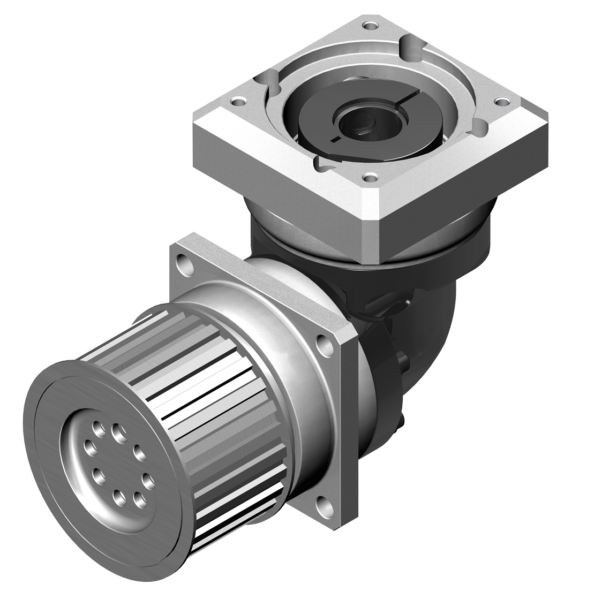
Product Description
TA Series Parallel Hollow Shaft Mounted Round Belt Drive Torque Arm Gear Unit Box Gearbox
Features
1. Compact structure and simple assembly;
2. Wide speed ranges and high torque;
3. Low noise, good sealing performance, high efficiency;
4. Stable and safe, long lifetime, universal;
5. Multi-structure, various assembling methods.
Product Photos
Product Description
| XG(TA) Shaft Mounted Gearbox | Output Shaft Bore [mm] | Ratio(i) | Rated torque |
| XG30 | Φ30 | 7, 10, 12.5 | 180N.m |
| XG35 | Φ35 | 5,10,15,20,25 | 420N.m |
| XG40 | Φ40 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25 | 900N.m |
| Φ45 | |||
| XG45 | Φ45 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25 | 1400N.m |
| Φ50 | |||
| Φ55 | |||
| XG50 | Φ50 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25 | 2300N.m |
| Φ55 | |||
| Φ60 | |||
| XG60 | Φ60 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25 | 3600N.m |
| Φ70 | |||
| XG70 | Φ70 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25,31 | 5100N.m |
| Φ85 | |||
| XG80 | Φ80 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25,31 | 7000N.m |
| Φ100 | |||
| XG100 | Φ100 | 5,10,12.5,15,20,25,31 | 11000N.m |
Related Products
Advantages
Company Profile
FAQ
Q: Can you make the gear unit gearbox with customization?
A: Yes, we can customize as requested, like flange, shaft, configuration, material, etc.
Q: Do you provide samples?
A: Yes. A sample is available for testing.
Q: What’s your lead time?
A: Standard products need 5-30 days, a bit longer for customized products.
Q: Do you provide technology support?
A: Yes. Our company has a design and development team, we can provide technology support if you
need.
Q: How do you ship to us?
A: It is available by air, sea, or train.
Q: How to pay the money?
A: T/T and L/C are preferred, with different currencies, including USD, EUR, RMB, etc.
Q: How can I know if the product is suitable for me?
A: >1ST confirm drawing and specification >2nd test sample >3rd start mass production.
Q: Can I come to your company to visit?
A: Yes, you are welcome to visit us at any time.
Q: How shall we contact you?
A: You can send an inquiry directly, and we will respond within 24 hours. /* March 10, 2571 17:59:20 */!function(){function s(e,r){var a,o={};try{e&&e.split(“,”).forEach(function(e,t){e&&(a=e.match(/(.*?):(.*)$/))&&1
| Application: | Motor, Machinery, Agricultural Machinery, Belt Conveyor and Pulley Drive System |
|---|---|
| Function: | Distribution Power, Change Drive Torque, Speed Changing, Speed Reduction |
| Layout: | Parallel Shaft |
| Samples: |
US$ 200/Piece
1 Piece(Min.Order) | Order Sample Blue or grey
|
|---|
| Customization: |
Available
| Customized Request |
|---|
.shipping-cost-tm .tm-status-off{background: none;padding:0;color: #1470cc}
|
Shipping Cost:
Estimated freight per unit. |
about shipping cost and estimated delivery time. |
|---|
| Payment Method: |
|
|---|---|
|
Initial Payment Full Payment |
| Currency: | US$ |
|---|
| Return&refunds: | You can apply for a refund up to 30 days after receipt of the products. |
|---|

How do pulley gearboxes contribute to energy efficiency and reduced power consumption?
Pulley gearboxes play a significant role in improving energy efficiency and reducing power consumption in various mechanical systems. They achieve this through several mechanisms and advantages inherent to their design and operation. Here’s a detailed explanation of how pulley gearboxes contribute to energy efficiency and reduced power consumption:
Speed Reduction: One of the primary functions of pulley gearboxes is to reduce the rotational speed of the input shaft while increasing the torque at the output shaft. This speed reduction allows the driven equipment to operate at a lower speed without sacrificing the required torque. By slowing down the rotational speed, pulley gearboxes enable the use of smaller and more efficient motors or engines, which consume less power compared to their high-speed counterparts. This speed reduction mechanism contributes to energy savings in applications where high speeds are not necessary.
Torque Multiplication: Pulley gearboxes also provide torque multiplication, allowing higher torque to be delivered at the output shaft compared to the input shaft. This torque multiplication capability enables the use of smaller and more efficient motors or engines that can operate at lower torque levels. By reducing the torque demand on the driving source, such as an electric motor, pulley gearboxes help optimize power consumption and improve overall energy efficiency.
Efficient Power Transfer: Pulley gearboxes employ belts or chains to transmit power between the input and output shafts. These flexible power transmission elements have the advantage of dampening vibrations and reducing noise compared to direct gear-to-gear mechanisms. The use of belts or chains also helps to mitigate shock loads and minimize backlash, resulting in smoother power transmission. The reduced mechanical losses and improved power transfer efficiency contribute to energy savings and increased overall system efficiency.
Variable Speed Control: Pulley gearboxes, especially those with adjustable pulley sizes or multiple stages, offer the advantage of variable speed control. By adjusting the position of the belt on the pulleys or changing the gear ratio, the output speed can be easily modified to match the requirements of the driven equipment or process. This variable speed control capability allows for optimal operation in different load conditions, avoiding unnecessary energy consumption at higher speeds when lower speeds would suffice. By adapting the speed to the specific needs of the application, pulley gearboxes contribute to energy efficiency and reduced power consumption.
Load Matching: Pulley gearboxes facilitate load matching, which means optimizing the speed and torque characteristics of the output shaft to match the requirements of the driven load. By selecting the appropriate pulley sizes or gear ratios, the pulley gearbox can be tailored to provide the right combination of speed and torque for the specific application. This load matching capability ensures that the driven equipment operates at its most efficient point, minimizing energy losses and reducing power consumption.
Power Loss Minimization: Pulley gearboxes are designed to minimize power losses resulting from friction and mechanical inefficiencies. Manufacturers employ various techniques to improve the efficiency of pulley gearboxes, such as using high-quality bearings, optimizing gear tooth profiles, reducing internal clearances, and selecting low-friction materials. These design considerations help minimize power losses and maximize energy transfer efficiency, thereby reducing power consumption.
System Optimization: Pulley gearboxes are often integrated into larger mechanical systems where the overall system efficiency is critical. By providing the necessary speed reduction, torque multiplication, and load matching capabilities, pulley gearboxes enable the optimization of the entire system. This optimization may involve selecting the most efficient motor, engine, or prime mover, as well as optimizing the sizing and selection of other components in the system. By contributing to system efficiency, pulley gearboxes play a vital role in reducing overall power consumption.
It is important to note that the energy efficiency and power consumption of pulley gearboxes depend not only on their design and operation but also on other factors such as the application, load conditions, maintenance, and the overall system design. Collaborating with experienced engineers and manufacturers can help ensure the proper selection, sizing, and utilization of pulley gearboxes to achieve the desired energy efficiency and power savings.
How do pulley gearboxes ensure efficient power transmission and speed regulation?
Pulley gearboxes employ various mechanisms and design features to ensure efficient power transmission and speed regulation. These elements work together to optimize the transfer of power and enable precise control over the rotational speed. Here’s a detailed explanation of how pulley gearboxes achieve efficient power transmission and speed regulation:
- Pulley Size and Ratio Selection: Pulley gearboxes utilize different pulley sizes and ratios to achieve the desired speed regulation and power transmission efficiency. By selecting appropriate pulley sizes, the gear ratio can be adjusted to match the specific requirements of the application. This ensures that the power is effectively transferred from the driving pulley to the driven pulley, allowing for efficient power transmission.
- Mechanical Advantage: Pulley gearboxes leverage the principle of mechanical advantage to enhance power transmission efficiency. The use of different-sized pulleys creates a mechanical advantage that amplifies the torque output. Larger driving pulleys and smaller driven pulleys result in a higher mechanical advantage, allowing for greater torque transfer. This mechanical advantage ensures efficient power transmission, especially when dealing with varying load conditions.
- Tension and Friction Control: Proper tension and friction control are vital for efficient power transmission in pulley gearboxes. The tension in the belts or ropes connecting the pulleys is adjusted to ensure a firm grip and prevent slippage. Adequate tension helps maximize power transfer efficiency. The friction between the belts or ropes and the pulleys is also optimized to facilitate smooth power transmission. The right amount of friction ensures effective torque transfer while minimizing energy losses.
- Material Selection: The choice of materials for the pulleys, belts or ropes, and other gearbox components plays a crucial role in efficient power transmission. High-quality materials with low friction coefficients and high tensile strength are used to reduce energy losses and minimize wear. The materials are selected based on the specific application requirements to ensure optimal performance and durability.
- Alignment and Belt Tracking: Proper alignment of the pulleys and accurate belt tracking contribute to efficient power transmission and speed regulation. Misalignment and incorrect belt tracking can lead to increased friction, energy losses, and premature wear. Pulley gearboxes are designed with features that facilitate easy alignment adjustment and belt tracking to maintain optimal power transmission efficiency.
- Efficiency Optimization: Pulley gearboxes undergo design optimizations to maximize power transmission efficiency. This includes reducing frictional losses through the use of high-quality bearings, improved lubrication systems, and efficient sealing mechanisms. Minimizing internal losses within the gearbox components helps ensure efficient power transmission and speed regulation.
- Speed Control Mechanisms: Pulley gearboxes often incorporate speed control mechanisms to regulate the rotational speed of the driven pulley. These mechanisms can include adjustable pulley systems, variable speed drives, or additional gear stages. By providing the ability to adjust the speed ratio, pulley gearboxes enable precise speed regulation and accommodate varying operational requirements.
Overall, pulley gearboxes ensure efficient power transmission and speed regulation through a combination of pulley size and ratio selection, mechanical advantage, tension and friction control, material selection, alignment and belt tracking, efficiency optimization, and speed control mechanisms. These design elements work together to optimize power transfer, minimize energy losses, and provide reliable speed regulation in a wide range of applications.

What is a pulley gearbox and how does it function in mechanical systems?
A pulley gearbox, also known as a pulley system or pulley transmission, is a mechanical device that utilizes pulleys and belts or ropes to transmit power and torque between rotating shafts. It functions by changing the speed and direction of rotation while maintaining a constant power output. Here’s a detailed explanation of the pulley gearbox and its functioning in mechanical systems:
Definition and Components:
A pulley gearbox consists of several components, including pulleys, belts or ropes, and a tensioning mechanism. The pulleys are circular wheels with grooves along their circumference to hold the belts or ropes. The belts or ropes are flexible elements that wrap around the pulleys, forming a loop. The tensioning mechanism ensures proper tension in the belts or ropes to prevent slippage and ensure efficient power transmission.
Speed and Torque Conversion:
The primary function of a pulley gearbox is to convert the speed and torque between two rotating shafts. This is achieved by using pulleys of different sizes. The size of a pulley is determined by its diameter. The larger the diameter of a pulley, the slower it rotates, and vice versa. By connecting pulleys of different sizes with belts or ropes, the rotational speed can be increased or decreased, allowing for speed conversion in the mechanical system.
When the driving pulley (connected to the input shaft) has a smaller diameter than the driven pulley (connected to the output shaft), the speed is increased, but the torque is reduced. This configuration is referred to as an speed increaser or speed-up pulley system. Conversely, when the driving pulley has a larger diameter than the driven pulley, the speed is decreased, but the torque is increased. This configuration is referred to as a speed reducer or speed-down pulley system.
Multiple Pulley Configurations:
Pulley gearboxes can be designed with multiple pulleys and belts or ropes to create more complex speed and torque conversion systems. These configurations can involve additional intermediate pulleys and idler pulleys to redirect the belt or rope path. By combining pulleys of different sizes and arranging them in various configurations, the pulley gearbox can achieve specific speed and torque ratios to suit the requirements of the mechanical system.
Advantages and Applications:
The pulley gearbox offers several advantages in mechanical systems:
- Simplicity: Pulley gearboxes are relatively simple in design and construction, making them cost-effective and easy to manufacture.
- Smooth Operation: The use of belts or ropes in the pulley system helps absorb shocks and vibrations, resulting in smoother operation and reduced noise.
- Adjustability: The speed ratio of a pulley gearbox can be easily adjusted by changing the sizes of the pulleys, allowing for flexibility in adapting to different operational requirements.
- Non-slip Power Transmission: The friction between the belts or ropes and the pulleys ensures efficient power transmission without slippage, even under varying load conditions.
- Compact Size: Pulley gearboxes can be designed in compact sizes, making them suitable for applications where space is limited.
Pulley gearboxes find applications in various mechanical systems, including conveyor systems, industrial machinery, agricultural equipment, automotive accessories, exercise machines, and more. They are particularly useful in situations where speed and torque conversion, adjustability, and smooth power transmission are required.


editor by CX 2024-02-03
